Analytics Transformation: Strategy & Roadmap
Analytics & Advance Analytics – Overview
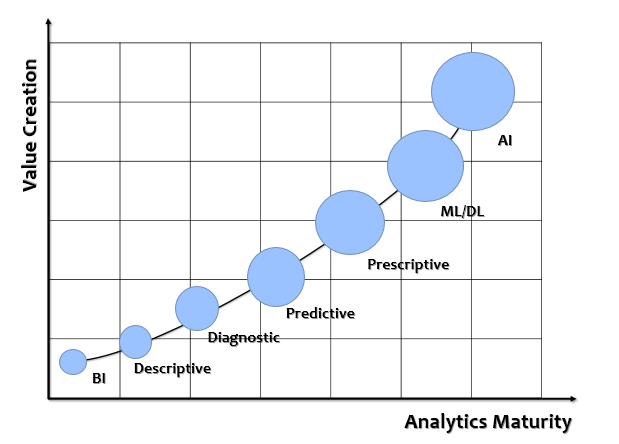
Business intelligence – BI: BI is the use of computing technologies for the identification, discovery and analysis of business data – like sales revenue, products, costs and incomes. BI technologies provide current, historical and predictive views of internally structured data for products and departments by establishing more effective decision-making and strategic operational insights through functions like online analytical processing (OLAP), reporting, predictive analytics, data/text mining, benchmarking and Business Performance Management – BPM.
Descriptive Analytics: As an analyst or a business owner, when you are looking for an answer of a question – What is happening in my business? This is when Descriptive analytics comes into place. It’s the most common and widely used analytics that analyses the data coming in real-time generally using effective visualisation tools like dashboards and allows us to learn from past behaviours and give us an idea about how they will impact future outcomes. But as it gives us only insight about whether everything is going well or not in our business, but it didn’t explain the root cause behind this. For this reason, highly data-driven businesses combine descriptive analytics with other types of data analytics to find the complete solution.
Diagnostic Analytics: When you already know what’s happening in your business using Descriptive analytics and you want to know that the answer of next question i.e. Why it is happening in your business or in general you want to know the root cause behind that, this is where Diagnostic analytics plays its part and helps analysts or data scientists to drill down inside the data to find the answer. Generally, in business, BI dashboards help you drill down using hierarchies or do a quick comparison to find the reasons or factors that are affecting business.
Predictive Analytics: Predictive Analytics is based on what you get from descriptive and diagnostic analytics and used to find answers to the question of what is likely to happen in the future based on previous trends and patterns? In general, it’s all about forecasting. Predictive Analytics utilizes various statistical and machine learning algorithms to provide recommendations and provide answers to questions related to what might happen in the future, that cannot be answered by BI. But as it’s probabilistic in nature, it just gives an estimate of a possible future outcome. Also, the accuracy is not 100% because it all depends on data quality, how you make educated guesses on the missing values and how optimization is done.
Prescriptive Analytics: When you get the findings from Descriptive, Diagnostic and Predictive analytics like what’s happened, the root cause behind that and what-might-happen in future, Prescriptive model utilizes those answers to help you determine the best course of action to choose to bypass or eliminate future issues. You can use Prescriptive analytics to advise users on possible outcomes and what they should do to maximise their key business metrics. The best example in front of you is Google Maps which helps you to choose the best route considering distance, traffic and speed.
Machine Learning / Deep Learning: Machine learning is loosely interpreted to mean empowering computer systems with the ability to “learn”. The intention of ML is to enable machines to learn by themselves using the provided data and make accurate predictions. ML is a subset of artificial intelligence; in fact, it’s simply a technique for realizing AI. It is a method of training algorithms such that they can learn how to make decisions. Training in machine learning entails giving a lot of data to the algorithm and allowing it to learn more about the processed information.
Deep learning is a subset of ML: in fact, it’s simply a technique for realizing machine learning. In other words, DL is the next evolution of machine learning. DL algorithms are roughly inspired by the information processing patterns found in the human brain. Just like we use our brains to identify patterns and classify various types of information, deep learning algorithms can be taught to accomplish the same tasks for machines. The brain usually tries to decipher the information it receives. It achieves this through labelling and assigning the items into various categories. Whenever we receive a new information, the brain tries to compare it to a known item before making sense of it — which is the same concept deep learning algorithms employ.
AI/Cognitive Analytics: Cognitive analytics combines a number of intelligent technologies like artificial intelligence, machine-learning algorithms, deep learning etc.to apply human brain like intelligence to perform certain tasks. Basically, this type of analytics is inspired by how the human brain processes information, draws conclusions and codifies instincts and experience into learning such as understanding not only the words in a text but the full context of what is being written or spoken. All these intelligent technologies make a cognitive application smarter and more effective over time by learning from its interactions with data and with humans.
| Attributes | Business Intelligence | Descriptive | Diagnostic | Predictive | Prescriptive | Machine/Deep Learning | Artificial Intelligence/ Cognitive |
| Perspective | Past | Past | Past | Future | Future | Future | Future |
| Type of Questions | What Happened | What Happened | Why Did it Happen | What could Happen | What should we do | Cause something to happen | How to enhance human reasoning |
| Method & Techniques | Reporting, Monitoring, Alerting, Dashboard, Scope Cards, OLAPs and Adhoc Queries | Data Mining, Data Discovery, OLAP, Adhoc Queries, Dashboards | Semantic & Sentiment Analysis, Data Mining, Modelling Statistics, OLAP, Decision Tree | Predictive Modelling, Neural Networks, Pattern Matching, Forecasting, Regression Analysis, Simulation, Alerts | Optimization Models, Heuristics, Discrete Choice Modelling, Linear / Non Liner Programming, Value Analysis, Graph Analysis | Natural Language Processing, Machine & Deep Learning, Training Data, Scoring, Labelling, Anomaly Detection | Cognitive Advisors, AI/DL, Automated resolution |
| Data | Structured | Structured | Structured & Unstructured | Structured, Unstructured & semi-structured | Structured, Unstructured & semi -structured | Structured, Unstructured & semi- structured | Structured, Unstructured & semi- structured |
| Knowledge Generation | Manual | Manual | Manual | Automatic | Automatic | Automatic | Automatic |
| Users | Business Users | Business Users | Business Users | Data Scientist, Business Analyst, Business Users | Data Scientist, Business Analyst, Business Users | Data Scientist, Business Analyst, Business Users | Data Scientist, Business Analyst, Business Users |
| Business Initiatives | Reactive | Reactive | Reactive | Proactive | Proactive | Proactive | Proactive |
| Output | Table | Table | Table | Table | Table | Answer | Answer |
| Scope | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Specific business question | Specific business question |
| Example Platforms/Tools | SAP BI, Cognos BI, Microstrategy BI, SAS BI, QlikView, Tableau BI, JasperSoft BI | SAP BI, Cognos BI, Microstrategy BI, SAS BI, QlikView BI, Tableau BI, JasperSoft BI | SAP, Cognos, SAS, R Enterprise, Tableau, JasperSoft | RapidMiner, KNIME, SAP Predictive Analytics, IBM Predictive Analytics, Microsoft R, SAS Predictive Analytics | SAP HANA, IBM SPSS, RapidMiner Studio, SAS Advanced Analytics, Radius | Google ML, Amazon ML, Amazon SageMaker, Accord.NET, Azure ML | Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit, Keras, TensorFlow, Theano, Caffe |
| Programming Language | R, Python, Java, SQL | R, Python, Java, SQL | R, Python, Java, SQL | R , Python, Java | R , Python, Java | Pyton, C/C++, Java, R, Javascript, TensorFlow | Python, R, Prolog, JAVA, C++ and LISP |
| Use Cases | Reporting, Dashboard | Measuring, Monitoring, KPI, | Trend Analytics, Situational Analysis, Root Cause, Cluster Analysis, Navigation, OLAP, Agile & Spatial Visualization | Forecasting, Probability Assessment, Risk Management Predications | Scenario based planning, strategy formulation & Optimization, Recommendation, Rule Systems, BPM Automation | Speech to Text, Text to Speech, NLP, Convesational, Translation, Sentiment Analysis | Image/Video Classification, Face Detection, Authentication, Visual Recognition, Process Control, Gesture Control, Robotics, Common Sense |
| Expertise | IT & Business Users | IT & Business Users, Business Analyst | Business Users, Business Analyst | Business Users, Business Analyst, Data Scientist | Business Users, Business Analyst, Data Scientist | Business Users, Business Analyst, Data Scientist | Business Users, Business Analyst, Data Scientist |
| Integration Complexity | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | High | High | High | High |
| Architecture | Batch | Batch | Batch | Batch / Real Time | Batch / Real Time | Real Time | Real Time |
| Limitations | Piling of Historical Data, Cost, Complexity, Limited use, Time Consuming Implementation | Piling of Historical Data, Cost, Complexity, Limited use, Time Consuming Implementation | Piling of Historical Data, Cost, Complexity, Limited use, Time Consuming Implementation | Expertise, Adoption, Empowering End Users, Burdensome Project Lists | Expertise, Adoption, Empowering End Users, Burdensome Project Lists | Provability, Data privacy and security, Algorithm bias, Data scarcity | Provability, Data privacy and security, Algorithm bias, Data scarcity |
About the Author
 Sameer Paradkar is an Enterprise Architect with 15+ years of extensive experience in the ICT industry which spans across Consulting, Product Development and Systems Integration. He is an Open Group TOGAF, Oracle Master Java EA, TMForum NGOSS, IBM SOA Solutions, IBM Cloud Solutions, IBM MobileFirst, ITIL Foundation V3, COBIT 5 and AWS certified enterprise architect. He serves as an advisory architect on Enterprise Architecture programs and continues to work as a Subject Matter Expert. He has worked on multiple architecture transformation and modernization engagements in the USA, UK, Europe, Asia Pacific and Middle East Regions that presented a phased roadmap to transformation that maximized the business value, while minimizing costs and risks.
Sameer Paradkar is an Enterprise Architect with 15+ years of extensive experience in the ICT industry which spans across Consulting, Product Development and Systems Integration. He is an Open Group TOGAF, Oracle Master Java EA, TMForum NGOSS, IBM SOA Solutions, IBM Cloud Solutions, IBM MobileFirst, ITIL Foundation V3, COBIT 5 and AWS certified enterprise architect. He serves as an advisory architect on Enterprise Architecture programs and continues to work as a Subject Matter Expert. He has worked on multiple architecture transformation and modernization engagements in the USA, UK, Europe, Asia Pacific and Middle East Regions that presented a phased roadmap to transformation that maximized the business value, while minimizing costs and risks.
Sameer is part of IT Strategy & Transformation Practice in AtoS. Prior to AtoS he has worked in organizations like EY – IT Advisory, IBM GBS, Wipro Consulting Services, TechMahindra and Infosys Technologies and specializes in IT Strategies and Enterprise transformation engagements.
Disclaimer
The views expressed in this article are the author’s views and AtoS does not subscribe to the substance, veracity or truthfulness of the said opinion.









Great article Sameer. The timing is good given the conversations on reporting and analytics that most organisations have underway.